Which laser marking technology is best: fiber, CO₂, or UV?

Sascha Ammesdoerfer
Videojet Director of Product Marketing
Laser marking technology, CO₂, fiber, and UV lasers, Heat-sensitive materials, Regulatory compliance and traceability, Permanent, high-contrast marks
Choosing the right laser marking technology depends on your materials, production needs, and application goals. CO₂, fiber, and UV lasers each excel in specific areas, from marking durable metals to coding heat-sensitive packaging.
Manufacturers often ask: “What’s the best laser for metal, plastic, glass, or films?” This guide compares CO₂, fiber, and UV lasers to help you decide.

What makes laser marking different from other coding technologies?
Laser marking stands out for its precision, durability, and efficiency. Unlike inkjet printers and labeling systems, lasers use a focused beam of light to create permanent, high-contrast marks directly on materials, without affecting the integrity of the package or its contents. This eliminates the need for inks, ribbons, or solvents, making lasers a clean, versatile, and cost-effective solution.
When should CO₂ lasers be used?

CO₂ lasers are the most versatile option for marking organic and non-metallic materials, such as cardboard, wood, glass, and certain plastics.
Key applications:
- Packaging: Mark variable information on cartons and labels using ablation to reveal contrasting material.
- Glass: Create durable, frosted marks for batch coding and decorative branding.
- Flexible films: Add scoring lines or marks for easy-tear packaging.
Advantages:
CO₂ lasers operate at infrared wavelengths, making them ideal for high-speed production in industries like food and beverage. However, they are not effective on metal unless it is pre-treated.
When are fiber lasers the best choice?
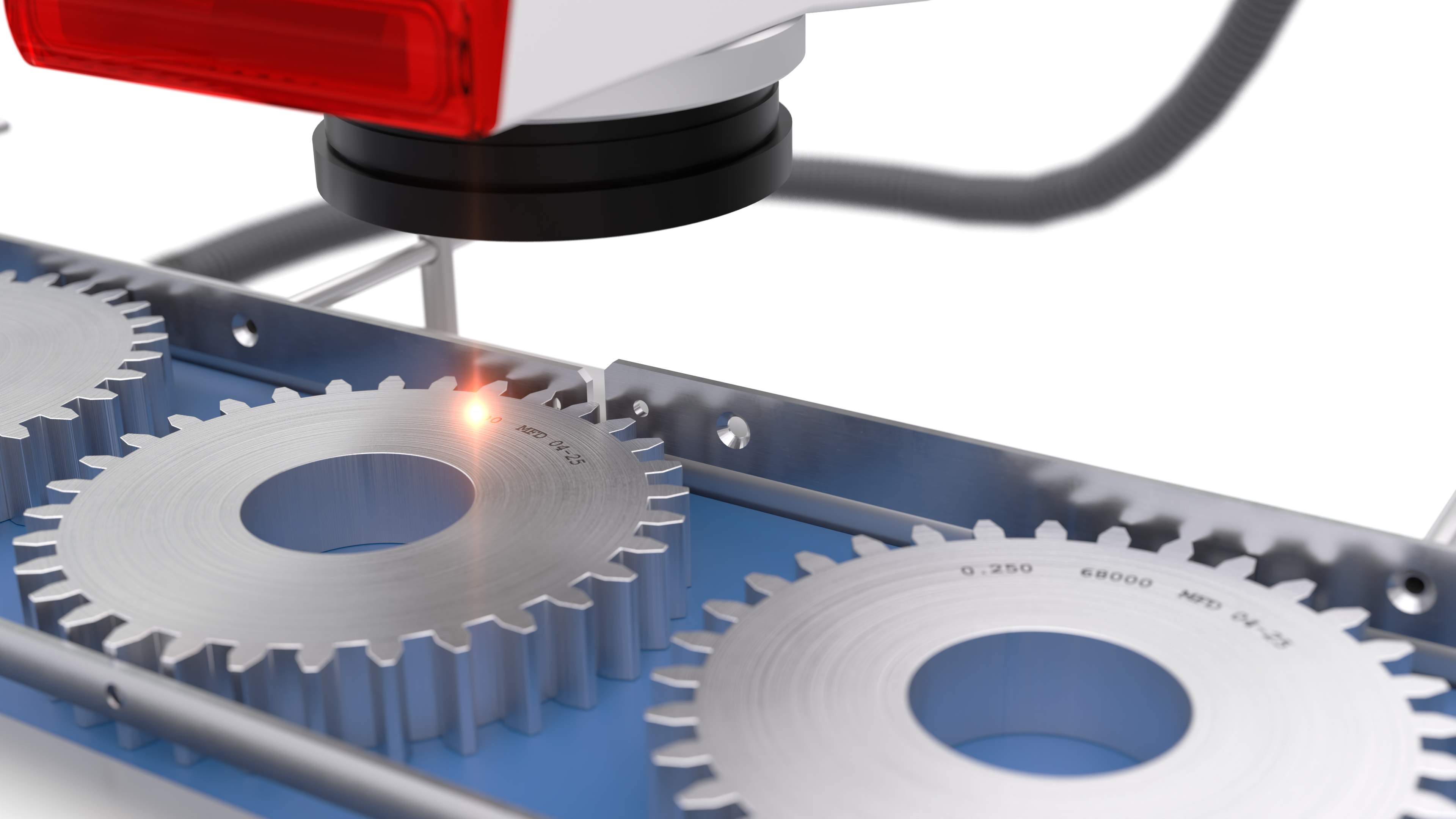
Fiber lasers are designed for marking durable materials, including metals and hard plastics, as well as certain flexible packaging.
Key Applications:
- Metals: Engrave serial numbers and codes on stainless steel, aluminum, and alloys.
- Plastics: Produce high-contrast marks on ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene, and more.
- Flexible packaging: Mark films and foils without requiring coatings or ablation.
- Food environments: With available IP69-rated marking heads, fiber lasers excel in washdown environments like meat processing plants.
Advantages:
Fiber lasers are highly precise, reliable, and cost-effective. They operate for up to 100,000 hours and mark metals without consumables, making them ideal for industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Why choose UV lasers for heat-sensitive materials?

UV lasers are the best choice for marking heat-sensitive and delicate materials, such as medical-grade plastics, flexible films, and glass.
Key applications:
- Healthcare: Mark syringes, blister packs, and medical devices with sterile, permanent codes.
- Electronics: Code delicate components like PCBs and microchips without thermal damage.
- Packaging: Mark films and foils without warping or damaging barrier properties.
- Glass and acrylic: Create high-contrast marks without microfractures.
Advantages:
UV lasers operate at shorter wavelengths, enabling “cold marking” with minimal heat impact. They require no consumables, aside from fume extractor filters, and excel in industries with strict quality and safety standards like healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
How do laser marking systems support regulatory compliance?
Laser marking systems produce durable, tamper-resistant marks that can meet global compliance standards for traceability and anti-counterfeiting.
Examples of compliance applications:
- Medical devices: Unique Device Identification (UDI) codes are required on a wide range of medical devices, including surgical tools, implants, syringes, and monitoring systems. These codes remain legible after repeated sterilization and are used to meet FDA and EU MDR requirements for traceability and patient safety.
- Pharmaceuticals: Lot codes, batch numbers, and expiration dates are marked on blister packs and other packaging to help comply with the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD), Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA), and other regulations. UV lasers can produce clear, durable codes without affecting the integrity of the packaging or its contents.

- Automotive and electronics: Permanent identification numbers and DataMatrix codes on components help enable lifecycle tracking and compliance with IATF 16949:2016 and other standards.
By delivering permanent, high-contrast, and machine-readable marks, laser marking systems help manufacturers meet traceability, anti-counterfeiting, and safety requirements across industries.
Choosing the right laser marking technology
Selecting the right laser marking system depends on your materials, production needs, and compliance requirements:
- CO₂ lasers: Best for organic and non-metallic materials like cardboard, PET bottles, and glass.
- Fiber lasers: Ideal for durable materials, such as metal and certain plastics, offering tamper-resistant marks.
- UV lasers: Perfect for heat-sensitive and delicate materials, such as flexible films, glass, and certain medical devices.
Laser marking is more than a coding solution—it’s an investment in precision, efficiency, and compliance. At Videojet, we specialize in helping manufacturers find the best-fit solution.
Why choose Videojet?
- Expert guidance to match the right laser technology to your application.
- Sample testing and integration support for seamless adoption.
- Proven solutions that enhance traceability and meet regulatory standards.
Let’s get started! Contact us today to explore how CO₂, fiber, and UV laser marking technologies can deliver lasting value for your business.
Go deeper
Videojet: Laser marking systems FAQs
Videojet: Comprehensive guide to choosing a laser marking system
Videojet: Part marking methods: laser and continuous inkjet
Videojet: Innovative techniques in medical device marking
Videojet: Laser marking systems
