FAQs: What is the best coding solution for automotive parts, packaging, and pallets?

Videojet Knowledge Hub Team
auto parts, part marking, compliance, product traceability, direct parts marking
The right coding solution delivers durable, readable codes that comply with industry standards, such as IATF 16949 and AIAG B-17, which set requirements for product safety, traceability, and quality in the automotive industry. Choosing the best option depends on factors like production speed, integration requirements, code durability, and the material being marked. Continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers and laser markers create reliable codes on a variety of surfaces, including metal, plastic, glass, cardboard, and shrink wrap. Thermal inkjet (TIJ) printers produce crisp, high-resolution codes on packaging materials like paperboard. For secondary packaging, large character inkjet printers and print-and-apply labelers (LPA) are ideal for marking cases and cartons. Pallet labelers employ LPA technology to label multiple sides of wrapped pallets.
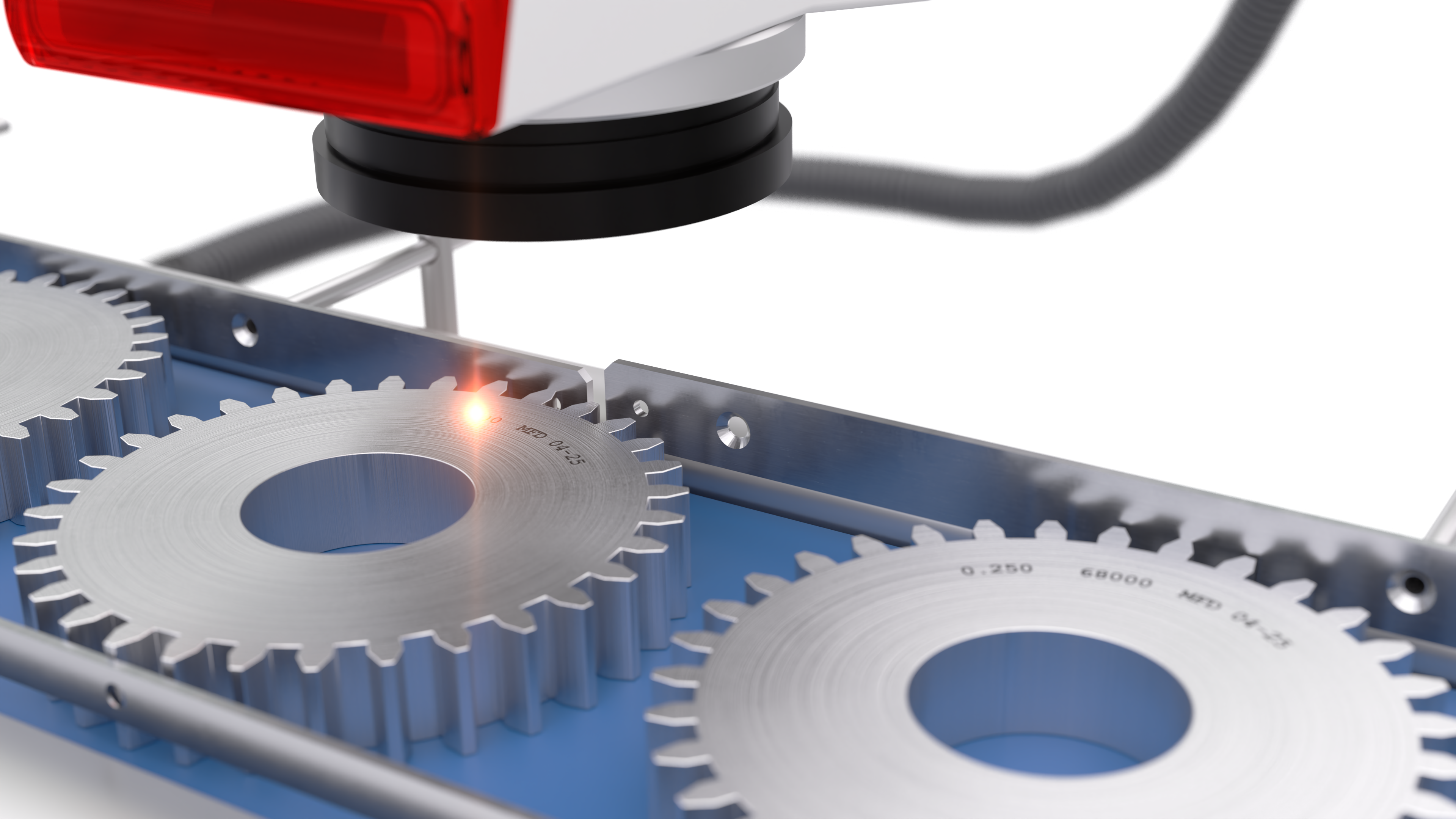
Traceability
Why is traceability crucial in the automotive industry and which regulations does it help meet in 2025?
Traceability coding helps manufacturers comply with standards, like ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and regional regulations, while enabling recall readiness.
- Regulatory compliance:
- Complying with safety requirements set by the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and similar organizations, and legislation such as the European Union’s General Product Safety Regulation to meet regional and international requirements for product safety, environmental standards, and reporting obligations.
- Enhanced quality control:
- Identifying and isolating defects quickly, minimizing production disruptions, and warranty claims.
- mproving overall product reliability by tracking components throughout their lifecycle.
- Efficient recall management:
- Enabling manufacturers to track and trace defective components, reducing the time and cost of recalls.
- Simplifying the process of identifying affected products to protect consumers.
- Brand protection:
- Building consumer trust by demonstrating a commitment to quality and safety.
- Safeguarding brand reputation by ensuring product integrity and compliance with regulations.
How do you make a part traceable?
Making an automotive part traceable involves creating and applying a unique, durable identifier and making it traceable by following these critical steps:
- Assign a unique identifier:
- Use a serial number, batch/lot code, or 2D code to create a “digital fingerprint” for the part to meet applicable regulatory and industry standards.
- Mark the part:
- Apply the machine-readable code using technologies like laser marking or continuous inkjet printing, depending on the material and application.
- Verify mark quality:
- Ensure the code meets readability and quality standards, such as ISO/IEC TR 29158 (AIM DPM) for direct part marking.
- Log data into a traceability system:
- Integrate the identifier into a centralized database or MES/ERP system for tracking throughout the supply chain.
- Ensure compliance:
- Adhere to industry standards, such as IATF 16949.
What traceability requirements do components and assemblies need to meet?
Every component and assembly must have a digital identity: a machine-readable, durable mark that stays with the product throughout its lifecycle. This digital identity is typically encoded in a DataMatrix 2D code that is directly marked onto the part.
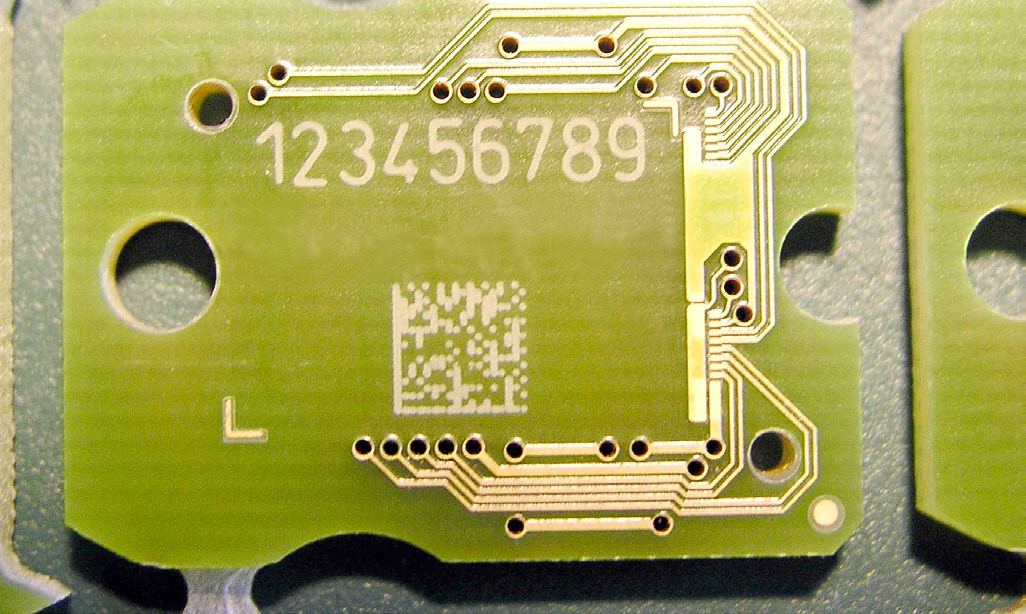
How do you ensure traceability for printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electronic components?
Traceability for PCBs starts at the beginning of the manufacturing process, with 2D codes and traceability data printed directly on the boards.
- Durability: Able to withstand reflow soldering and conformal coatings.
- Code type/size: Compact and high-resolution alphanumeric and 2D codes like DataMatrix and QR codes®
- Common standards: IPC-1782 and MIL-STD-130
- Process: Print, mark, verify, and log into MES
What do manufacturers need to meet modern traceability requirements?
To meet today’s traceability demands, manufacturers need:
- Robust marking systems: Help ensure durability and readability of marks over the product’s lifecycle.
- Standards-compliant solutions: Systems must meet industry-specific regulations for data and marking quality.
- Integrated data infrastructure: Seamless integration with MES/ERP systems for real-time serial number generation, mark quality verification, and scan result logging—all without disrupting production throughput.
Variable codes
What are the most common methods used to add variable codes to products?
Laser marking and continuous inkjet printing are common methods for adding variable codes to products.
- Laser marking: Delivers precise, permanent marks.

- Continuous inkjet printing: Flexible and cost-effective.

Marking on metal and plastic
What is the best way to mark on castings and metal components?
Laser etching, annealing, and engraving processes produce permanent codes on metal parts during production, typically after molding.
- Laser etching: Creates a fine surface contrast by affecting the top 2–20 µm of material.
- Laser annealing: Forms a colored oxide layer without altering the material surface.
- Laser engraving: Produces deep, durable marks (30–300 µm) that withstand harsh conditions.

How do you mark on plastic parts in the automotive industry?
Technologies for marking plastic components include laser marking systems and continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers for durable alphanumeric, logos, symbols, and barcodes on hard and flexible plastics.

2D codes
What are the industry standards for 2D codes in automotive industry?
Automotive industry standards for 2D codes include:
- AIAG B-17: The AIAG B-17 standard, also known as the 2D Direct Parts Marking Guideline, focuses on parts identification methods using DataMatrix and QR code symbols. You can find more information and purchase options here: https://www.aiag.org/store/publications/details?ProductCode=B-17
- IATF 16949: This standard defines quality management system requirements for the automotive industry. Learn more and access resources here: https://www.aiag.org/quality/iatf-16949

Choosing a solution
How do you choose the right printing or marking technology for coding automotive parts and packaging?
When selecting the best coding technology, three key factors should be considered:
- Line speed: Ensure the coding technology can keep up with production speeds without compromising quality.
- Substrate material: Consider the product, part, or packaging material and how the coding technology (laser or ink) will interact with it.
- Integration space: Assess the available space for incorporating the marking solution into your existing production line.
Here’s a look at the top solutions for printing and marking on automotive parts and packaging
- CIJ printing Continuous inkjet (CIJ) printing is popular for its ability to print on various materials in automotive manufacturing, including castings, metal and plastic components, and electronics, as well as flexible packaging. It offers a low cost per print, high-speed operation, and a wide range of inks.
- Laser marking Laser marking systems create high-quality images on various materials without inks or chemicals. They come in different wavelengths (infrared to ultraviolet) and power outputs, suitable for nearly any application. Videojet lasers can meet IP54 and IP69 standards for harsh conditions.
Printing on packaging
- TIJ printing Thermal inkjet (TIJ) printers provide high-resolution printing (up to 600 dpi) with minimal maintenance. They can print text, barcodes, and 2D codes on various packaging materials, making them ideal for traceability applications.
- TTO printing Thermal transfer overprinters (TTO) are perfect for adding variable information to bags, pouches, and labels in automotive packaging. The Videojet 6530 and 6330 printers feature iAssure™ technology for automatic code checks and handle a range of applications from simple date coding to 2D codes powered by GS1.
- Large character marking (LCM) LCM printers can apply text, logos, and barcodes directly on secondary packaging like shipping cases. The Videojet 2380 features a self-cleaning printhead and prints up to 70mm high per head. It supports both Ethernet connectivity for easy integration and Wi-Fi for remote access and analytical capabilities.
- Print and apply labeling The Videojet 9560 print and apply labeler is designed for high-speed packaging lines, applying labels to cases, boxes, and shrink-wrapped trays. Direct Apply™ technology reduces label jams and downtime.
- Pallet labeling The Videojet 9560 PL pallet labeler can print and apply up to four labels per pallet at speeds up to 120 pallets per hour. Intelligent Motion™ technology maximizes uptime and simplifies label and ribbon replenishment.
Why choose Videojet for automotive parts, packaging, and pallet coding?
Videojet specializes in automotive parts coding solutions that meet the industry’s demands for speed, precision, and compliance.
Use continuous inkjet (CIJ) for high-speed lines and varied substrates—CIJ delivers flexible, cost-effective coding suited to dynamic automotive production.
For permanent codes that support long-term traceability on metals and engineered plastics, apply laser marking systems with minimal maintenance requirements. Use large character marking (LCM) and print-and-apply labeling systems for cases, and pallet labelers specifically for pallets, to meet packaging and logistics standards.
Across all coding technologies, integrate CLARiSUITE® Code Assurance to control data and templates, and activate Videojet Remote Service for real-time diagnostics and operator support. These tools help reduce coding errors, simplify compliance, and support production goals with confidence.
Go deeper
Videojet: Part marking methods: laser and continuous inkjet
Videojet: Automotive and aerospace part marking
VideojetConnect® Remote Service
VideojetConnect CLARiSUITE®
QR Code is a registered trademark of DENSO WAVE INCORPORATED.
